Abstract
The use of financial robo-advisors based on artificial intelligence has a great impact on the financial technology industry, providing personalized investment services, and changing the UX in the field of fintech applications. This paper aims at discussing robo-advisors and their impact on UX/UI design, with an emphasis on the optimization of engagement, trust, and satisfaction. It talks about the prospects and the difficulties of UX/UI designers in developing understandable, accessible, and user-oriented financial applications that can benefit from the use of AI.
Introduction
Fintech has become one of the most rapidly growing industries due to technological development and the increasing demand for digital solutions for personal and business needs. The key driver of this transformation is the AI-based financial robo advisor, which represent the intersection of artificial intelligence and financial services that offer algorithm-based financial planning services with little human intervention. These digital advisors have offered low-cost, efficient accessible financial advisory services to the common people, which was earlier a luxury of the rich. The effectiveness of the fintech applications, especially those that include AI components such as robo-advisors, is highly dependent on the user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design.
A well-designed UX/UI not only simplifies the complexity inherent in financial services but also engenders trust and fosters long-term user engagement. When it comes to financial robo advisor, the UX/UI design has to take complex algorithms and present them to the user in a way that allows them to make effective financial choices. This paper seeks to examine the incorporation of robo-advisors in fintech applications through the lens of UX/UI design. It will discuss how the principles of good design can be applied to these digital advisors to improve usability and aesthetics, the issues arising from the implementation of AI in the financial sector, and where UX/UI designers can play a role. Analyzing the connection between AI and UX/UI design, the paper will outline the important aspects of designing effective fintech applications, which will be appreciated by users and will have a competitive advantage in the market.
Fintech Revolution & the Role of UX/UI Design
The transition from traditional banking to digital fintech solutions marks one of the most significant shifts in the financial industry’s history. This transformation has been brought about by various factors such as technology, customer demands, and a favorable legal framework. Consequently, conventional financial institutions have been forced to redefine the way they offer services and a new generation of fintech companies has appeared on the market with innovative, customer-oriented services. Fintech revolution cannot be complete without the involvement of UX/UI design. It is the link between the raw financial information and the consumer, changing the way consumers engage with financial products.
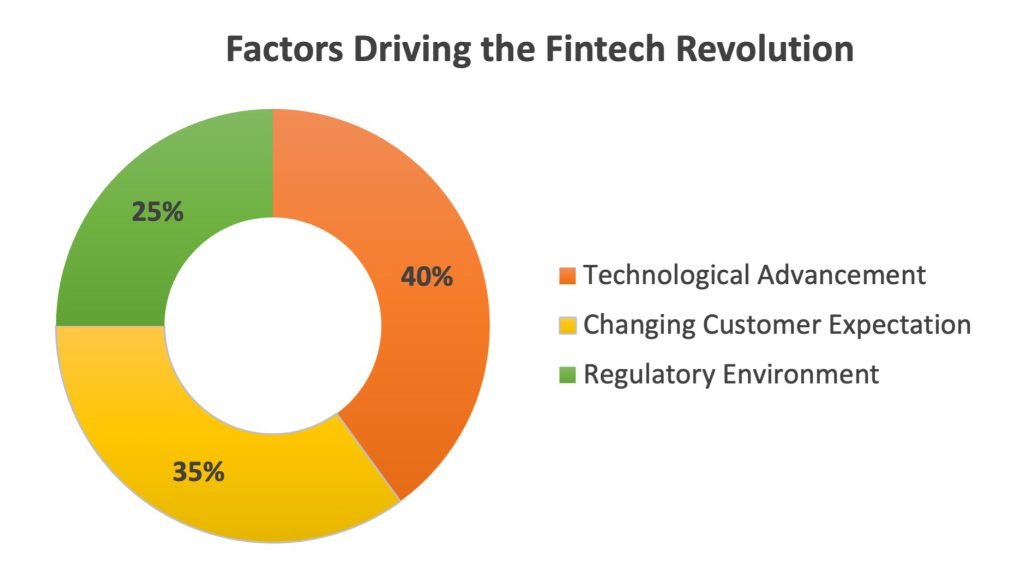
The design of a fintech application can significantly influence user adoption by providing intuitive navigation, clear information architecture, and a visually appealing interface that simplifies the user journey. However, user experience design is not just about aesthetics; it is the whole process of obtaining and implementing the product, with branding, design, usability, and functionality. Fintech UX is different from that of other industries as well as offers distinct possibilities. Designers must navigate the intricacies of financial regulation, data security, and privacy while creating an experience that is both engaging and reassuring. They also have to take into account the level of financial literacy of the target audience and make sure that the application is easy to use and the information is comprehensible. The opportunity consists in adopting design thinking to develop solutions that go beyond the client’s needs and promote the use of fintech services.
How do AI-Powered Financial Robo Advisor Work
Robo-advisors are one of the biggest disruptions in the field of personal finance and investment, offering automated, data-driven advice that is both scalable and cost-effective. These digital platforms use algorithms to analyze user data, assess risk tolerance, and automatically allocate and manage investments. The functionality of robo-advisors are not limited to portfolio management but also include users’ financial assessment, including budgeting, retirement planning, and savings. The addition of financial robo advisor applications has significantly changed the dynamics of personal finance management. They have made financial advice accessible to a broader audience, offering a level of personalization and ease that was once beyond the reach of the average person. However, the success of these platforms relies on their ability to deliver an efficient user experience.
There are several factors to consider when it comes to the user experience design of robo-advisors. Information architecture is critical, as it dictates how information is structured and presented to the user. A well-designed information architecture helps users understand their financial status and the recommendations provided by the financial. Another important aspect is interaction design, which deals with how the application is used by the users. This includes the design of the interface, interactive elements, and the user flow of the application. Another aspect is the visual design since it includes the use of color, typography, and imagery to ensure that the interface is visually appealing and easy to understand while conveying trust and professionalism. When designing the UI/UX of robo-advisors, designers must consider the balance between automation and user control. The users should have an impression that they are in charge of their financial decisions even though the robo-advisor is advising them. This balance is made possible by good design that presents the users with clear choices, informs them how their money is being managed and allows them to override the automated decisions if they wanted.
Building Trust through UX/UI Design in Financial Robo Advisor
In the context of fintech, trust is the foundation of user adoption and retention. In the context of fintech, trust is the foundation of user adoption and retention. For AI robo-advisors where the user relies on the algorithm to manage their finances the user interface becomes a critical factor in building and sustaining that trust. Good UI/UX design can help to make even complicated systems look easy to use and trustworthy, thus making the user engage with the technology. This suggests that transparency is an important design strategy in creating the right amount of trust.Users have to know how robo-advisors work and what decisions and actions are made with their investments. Such an approach makes it easy for users to understand their position in terms of finances as well as the outcomes of robo-advisorsers to understand their position in terms of finances as well as the outcomes of robo-advisor actions.
Interactive charts, personalized dashboards, and straightforward explanations of investment strategies can demystify the AI processes and reassure users about the safety and rationale behind their investments. Another dimension of transparency is enabling the user to have the power to override the decision made by the AI. This can be done with help of options to limit investments, select the level of risk, and make the last decision concerning the proposed financial actions. Thus, such elements help to achieve the goal of engaging the user and, at the same time, to create the partnership between the user and the robo-advisor.
An example of this is the design strategy employed by Betterment, one of the most popular robo-advisors in the market. Betterment has a simple and uncluttered design that helps the users to see their investment portfolio, growth estimates, and recommendations from financial experts, all without any complicated terms. The ‘check-in’ and alerts are scheduled and occasional, so the users are always aware of their portfolio performance, thus constant reassurance. Another giant of the industry, Wealthfront, uses Path, a set of visual sliders that let the client change goals and see the result at once. Apart from providing information about investment plans, this feature also helps to enhance the clients’ trust as it shows the immediate results of their decisions.
Personalization and Predictive User Interfaces
AI is the key enabler of the personalization features of financial robo-advisors which make it possible for the systems to provide a client-specific approach to financial management. By analyzing the large amounts of data, including spending habits, savings goals, and risk tolerance, AI is able to design a customized investment plan that reflects the user’s financial status and goals. This goes a notch higher than just personalization as predictive analytics is able to go a step further and predict the need of the user before he or she explicitly stated. For example, if a user has been putting a part of his/her monthly earnings into investment, the financial robo advisor can assume such a pattern and recommend an automatic investment plan. Predictive user interfaces are to notify the user of a potential financial opportunities or risks, such as a significant market change that might affect their portfolio.
However, with great personalization comes the challenge of maintaining user privacy. More and more people are aware of data usage and are worried about it. These issues can be resolved through user experience design by including options that enable the user to regulate what information is shared with the robo-advisor. When the privacy settings are well designed and easily understandable, along with the usage of data, minimising the level of personalisation can make the users comfortable.
One way of achieving this balance is by looking at the design of the robo-advisor application known as Ellevest. It offers the service of choosing an investment profile based on parameters like gender, salary, and life expectancy, which may be different from the standard ones. To enforce the users’ control over their data, Ellevest’s design provides users with concise explanations of why specific pieces of personal information are collected and how they affect the financial advice given by the app. Therefore, it can be concluded that the UX/UI design of robo-advisors is essential to creating trust due to the openness and individual approach while at the same time following the principles of privacy. Therefore, the processes which are based on AI and present the user with an individualized forecast while maintaining control over the data allow fintech applications to build a reliable and stimulating user experience.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Fintech UX/UI Design
Innovative approaches to development of the fintech solutions should be implemented to create applications that can be comfortable for disabled people. Accessibility in the context of fintech is not only in meeting certain standards but in designing the interface and the surroundings in a way that will allow every individual to easily interact with the application. This approach is essential for improving financial inclusion and ensuring that people with disabilities have equal access to financial services and products. The principles of universal design focus on developing products and surroundings that can be used by everyone to the greatest extent possible. In the case of fintech UX/UI design, this entails providing for features that would appeal to as many users as possible. For instance, the high-contrast colors, the contrast of the shades, the reader for the blind, and text-to-speech options can make platforms more accessible for users with visual impairments. In the same way, including closed captioning and transcripts for videos and audio content can enhance the accessibility for the users with hearing impairments.
It is possible to enhance the usability of platforms for people with physical disabilities by applying the principles of keyboard shortcuts and minimizing mouse usage. Further, literate language, the ability to change the font, and color contrast are crucial for people with cognitive impairments or poor literacy. These features also contribute towards the accessibility as well as the usability of the site from a larger perspective. An example of accessible design at work is the integration of screen reader compatibility and voice-guided navigation in applications for money transfers. These features disentangle limitations to visually impaired users to enable them to comfortably use the app to transfer funds and receive feedbacks through their screen readers. Another example is the additional of the touch gestures and the clickable area which can be enlarged for the persons with the motor disabilities. Therefore, through integrating the principles of accessibility in the products they are developing, the fintechs will be able to offer more effective and efficient financial solutions that could be helpful for all the stakeholders. This approach not only helps in creating a more inclusive society, but also helps in overcoming the digital gap, because the platform is created so that any person with different levels of digital competence can use it. In conclusion, the improvements for the users’ quality of lives are the reasons why the design for the financially impaired should be valued in this constantly developing area of fintech.
Iterative Design and Continuous User Feedback
The iterative design process is crucial in the fintech UX/UI design since the robo-advisors can be updated frequently based on the users’ feedback. This way, the application is developed in a way that responds to the needs and expectations of the users so it becomes more usable. User feedback is integrated into the design process through various methodologies, including A/B testing, usability testing, and analytics. A/B testing is a process of comparing two versions of a design to find out which one out of that two design is more effective in delivering results in terms of usability and satisfaction. This method provides valuable insights into user preferences and can help the designers in deciding which aspects of the design should be retained or changed.
Usability testing mainly focuses on the user and how he or she uses the financial robo advisor; it helps in identifying areas of discomfort or areas that need to be changed. Ideally, this method enables the designers to see the user’s view and enable appropriate changes to be made for the sake of improving the user’s experience. Analytics provide quantitative data on user interactions, allowing designers to track users’ behavior and look for trends or patterns. Such data can be used in design decisions and guide what aspects or changes will have the greatest impact on the user experience. By integrating the user feedback into the design process, the fintech companies can develop more user-centered applications that will be more useful for the users. This approach not only improves the usability of the application but also fosters a sense of ownership and engagement among users, as they see their feedback being taken into account.
An example of such iterative design is seen in the constant evolution of robo-advisors such as Betterment and Wealthfront. These platforms are constantly evolving their aesthetics, as well as the functionalities that they offer, based on the needs of the users. For instance, Betterment’s periodic “check-ins” and alerts are a result of user feedback, that made the company realize the importance of communicating portfolio performance on a regular basis.
Conclusion
In this research, the implementation of financial robo-advisors in the fintech context has been examined with a specific focus on the UX/UI perspective. These include the need to establish trust and user control as well as the need for personalization and predictive user interfaces and designing for all. The iterative design process and the constant feedback from the users are also essential in enhancing and developing robo-advisors.